Sports injury treatment
Sports injuries are a common occurrence among athletes and active individuals, caused by factors such as overuse, improper technique, accidents during physical activity, and inadequate protective gear. Common sports injuries include sprains, strains, tendonitis, Tennis elbow, Golfers elbow, Plantar fasciitis, and others. Proper treatment and rehabilitation are essential to ensure full recovery and prevent recurring injuries.
Common Types of Sports Injuries
A sprain occurs when a ligament, which connects bone to bone, is stretched or torn. This can cause pain, swelling, and bruising.
A strain occurs when a muscle or tendon, which connects muscle to bone, is stretched or torn. This can cause pain, weakness, and limited mobility.
A fracture occurs when a bone is broken or cracked. This can cause severe pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected area.
A dislocation occurs when a bone is forced out of its normal position, usually as a result of trauma. This can cause intense pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons, which connect muscles to bones. This can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving the affected area.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) and golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) are both forms of tendinitis that affect the elbow. They are caused by repetitive wrist and forearm motion and can be particularly common in racket sports such as tennis and golf.
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, becomes inflamed or irritated. It is often caused by repetitive strain on the foot, such as running or walking long distances, standing for extended periods of time, or wearing poorly fitting shoes.
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions and lubricates joints. This can cause pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
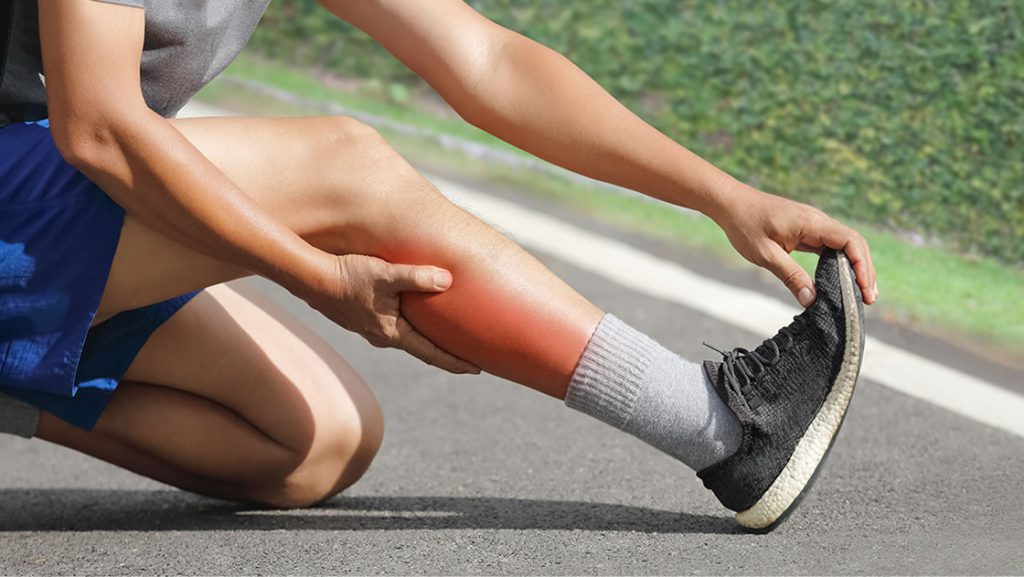

Treatment options for sports injuries depend on the type and severity of the injury, but may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), medication, physical therapy, or surgery. In recent years, Class 4 laser therapy has emerged as an effective treatment option for managing sports injuries. The therapy uses a high-powered laser light to penetrate deep into the tissue and stimulate cellular activity, which can help reduce inflammation, promote healing, and provide pain relief. Photobiomodulation, also known as Class 4 laser therapy, is helping athletes return to the field more quickly. By administering the laser to the affected area as soon as possible, pain relief can be achieved faster, and the healing process can begin sooner.
Benefits of Class 4 Laser Therapy for Sports Injuries
Class 4 Laser Therapy has many benefits in treating sports injuries, including:
- Reduction in pain, inflammation, and swelling associated with the injury
- Acceleration of tissue repair and regeneration for faster healing times
- Improvement in range of motion and flexibility, allowing athletes to return to their sport more quickly
- Noninvasive nature of the therapy compared to traditional methods such as medication and surgery
- Minimal side effects and natural healing process, potentially eliminating the need for long-term medication use
- Potential applications beyond sports injuries, making it a versatile and promising therapy in various medical fields.
Relief of Inflammation, Injuries, and Pain
Class 4 laser therapy has emerged as an effective treatment option for managing these types of injuries. The therapy uses a high-powered laser light to penetrate deep into the tissue and stimulate cellular activity, which leads to increased circulation, reduced inflammation, and accelerated tissue repair.
Class 4 therapeutic lasers can effectively alleviate inflammation, injuries, and pain. The key mechanism underlying their effectiveness is photobiomodulation (PBM), which involves the absorption of photons in red and infrared laser light by chromophores. These lasers are FDA-cleared medical devices that are capable of providing treatment to a large volume of tissue in individuals with sports injuries.
The specific wavelength and parameters used during Class 4 laser therapy will depend on the type and location of the injury, as well as the patient’s individual needs. Generally, shorter wavelengths (such as 635nm) are used for superficial injuries, while longer wavelengths (such as 1064nm) are used for deeper tissue penetration.
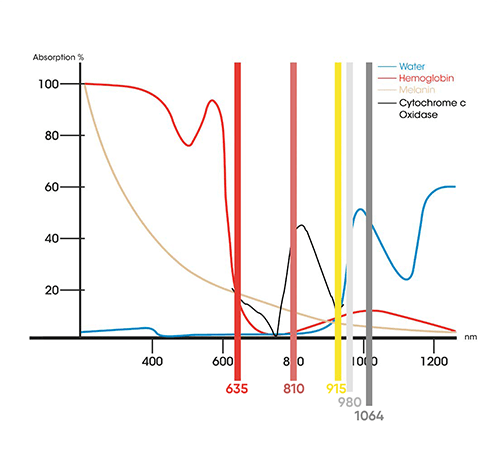


For sprains and strains, Class 4 laser therapy can help reduce inflammation and pain, while promoting healing of the affected tissue. For tendonitis, the therapy can help increase blood flow to the affected area and promote collagen production, which is essential for repairing damaged tendons.
For conditions like Tennis elbow, Golfers elbow, and Plantar fasciitis, Class 4 laser therapy can help reduce pain and promote healing by stimulating cellular activity in the affected area.
Plantar fasciitis is one such condition that can be treated using Class 4 therapeutic lasers. Sarah Lee, an expert in sports medicine, has noted that a combination of laser therapy, bracing, taping, and strengthening exercises can be used to alleviate inflammation and pain associated with this condition. She also emphasizes that, for proper treatment, patients should receive between 2,400-4,800 joules of energy at a surface dosage of 4-8 joules per centimeter squared.
Interestingly, these lasers have proven popular among college athletes who often have a limited playing career. Laser treatments can help reduce pain, inflammation, and promote healing, thereby improving the chances of elite athletes returning to competition more quickly. Overall, Class 4 therapeutic lasers offer a natural, non-invasive approach to treating sports injuries, providing pain relief and promoting tissue repair.
Overall, Class 4 laser therapy offers a safe, non-invasive, and convenient option for treating sports injuries. By using specific wavelengths and parameters tailored to each patient’s individual needs, this therapy can provide significant pain relief, improved mobility, and faster recovery times compared to traditional treatments alone.
“In my service to some of the top athletes in the country, I have witnessed all types of injuries, from acute trauma to repetitive use, from head to toe and superficial to deep. I have also been educated and exposed to all forms of treatment for sports injuries, including modalities, bracing and taping techniques, rehabilitative exercise and more.
It works really well on soft tissue injuries; we see a lot of those in the training department. Whether it is contusions, sprains, strains, or other soft tissue injuries, we have found that the sooner we get the laser on the area, the faster they get out of pain and the injury heals.
From the cases we have had in our practice I can say I’d strongly recommend the class 4 laser system. Its lovely for us to see the improvements with our athletes.”
——Emily Cooper,Athletic Trainer-April,2023
Scientific Support
Abstracts Worth Recommending
[1] Parr, J. J., Larkin, K. A., & Borsa, P. A. (2010). Effects of class IV laser therapy on exercise-induced muscle injury. Athletic Training & Sports Health Care, 2(6), 267-276.Larkin, K. A., Martin, J. S., Zeanah, E. H., True, J. M., Braith, R. W., & Borsa, P. A. (2012). Limb blood flow after class 4 laser therapy. Journal of athletic training, 47(2), 178-183.
[2] Kaub, L., & Schmitz, C. (2023). Spread of the Optical Power Emission of Three Units Each of Two Different Laser Therapy Devices Used in Sports Medicine, Which Cannot Be Assessed by the Users, Shown by Means of High-Fidelity Laser Measurement Technology. Biomedicines, 11(2), 585.
[3] Szabo, D. A., Neagu, N., Teodorescu, S., Predescu, C., Sopa, I. S., & Panait, L. (2022). TECAR Therapy Associated with High-Intensity Laser Therapy (Hilt) and Manual Therapy in the Treatment of Muscle Disorders: A Literature Review on the Theorised Effects Supporting Their Use. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6149.
[4] Tonk, G., Kumar, A., & Gupta, A. (2014). Platelet rich plasma versus laser therapy in lateral epicondylitis of elbow. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 48, 390-393.
[5] Bolin, D. J. (2003). Transdermal approaches to pain in sports injury management. Current Sports Medicine Reports, 2(6), 303-309.
[6] Roberts, D. B., Kruse, R. J., & Stoll, S. F. (2013). The effectiveness of therapeutic class IV (10 W) laser treatment for epicondylitis. Lasers in surgery and medicine, 45(5), 311-317.
THE SCIENCE AND EVIDENCE BACK IT
Laser therapy in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy: a pilot study. Photomedicine and laser surgery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18248158/
Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30572425/ligh
Laser therapy of muscle injuries. Lasers in medical science
Medical lasers
Professional CLASS 4 high-power laser therapy machine
Home use
Portable handheld cold laser therapy device
Veterinary use
Laser therapy machine, shockwave physical therapy, widely used in animals