LASER THERAPY FOR INFLAMMATION
A number of researches have revealed over 30% of people worldwide are troubled by inflammation, which remains a major concern for general public. Class 4 laser therapy has been proven to be a safe and effective treatment option for inflammation. It uses a high-powered laser to penetrate deep into the tissue, promoting cellular metabolism and reducing inflammation around joints. Inflammation may be associated with many diseases, such as arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, herniated disc and frozen shoulder.
CLINICALLY USED FOR
Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects the hands and wrists, caused by pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist made up of bones and ligaments. It contains the median nerve and tendons that control movement in the fingers.
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped, bulging, or ruptured disc, is a condition that occurs when the soft center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the exterior. When a disc herniates, the soft center can push out and compress nearby nerves, causing pain, weakness, tingling, or numbness in the affected area. Herniated discs most commonly occur in the lower back (lumbar spine) or neck (cervical spine).
A frozen shoulder is one that has become stuck and limited in movement. Frozen shoulder is often caused by inflammation of the capsule, tissue surrounding the shoulder joint. Diagnosing frozen shoulder requires a physical examination and possible X-rays or additional tests to rule out other causes of symptoms.
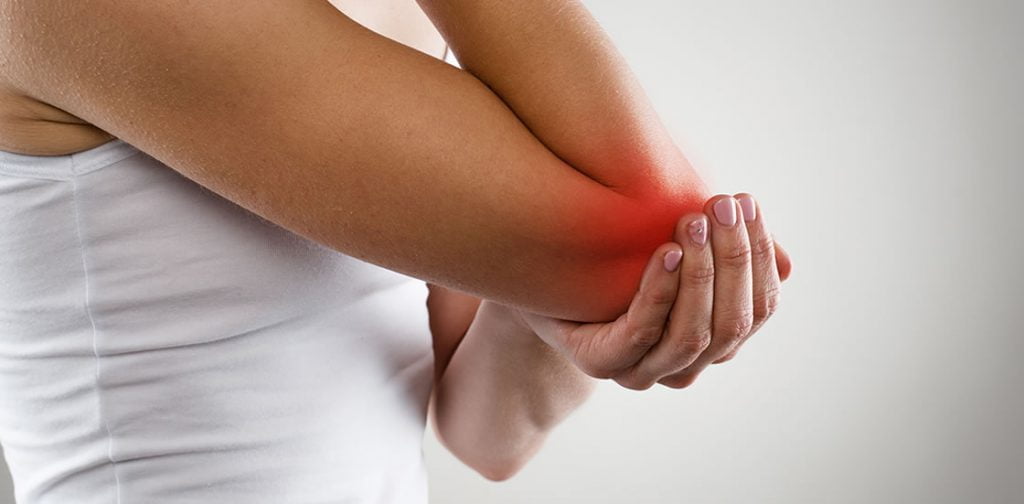
Inflammation is a normal part of the body’s response to injury or infection. Inflammation occurs when the body releases chemicals that trigger an immune response to fight off infection or heal damaged tissue. Once the injury or infection is healed, the inflammatory process ends.
What are the treatment options for inflammation?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation, while exercise, stretching, and massage therapy can help improve range of motion and reduce muscle tension. Additionally, applying cold or heat to the affected area can help promote healing and relieve pain. Eating a healthy diet and managing stress can also help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. Above all, laser therapy has gained much popularity among pain patients due to its non-invasive, pain-free and drug-free features. It has been widely applied in hospitals, clinics and rehabilitation center.
How does laser therapy reduce inflammation?
Laser therapy reduces inflammation by stimulating cellular activity and improving blood flow to the affected area. When high-level laser energy is applied to damaged tissues, it penetrates deep into the cells and stimulates the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary source of energy for cellular activities. The increased production of ATP can enhance cellular metabolism and promote tissue repair and regeneration. Laser therapy also increases the release of nitric oxide, which helps improve blood flow to the affected area, reducing inflammation and swelling.
Benefits of class 4 laser therapy for inflammation
- Reduced inflammation: reduce inflammation by stimulating cellular activity and promoting tissue repair.
- Pain relief: relieve pain associated with inflammation by blocking pain signals transmitted by nerve fibers.
- Faster healing: promote faster healing by enhancing cellular metabolism, improving blood flow and reducing scar tissue formation.
- Non-invasive: Class 4 laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment option that does not require medication or surgery, making it a safe and attractive alternative to traditional treatments.
- Precise treatment: target specific areas of inflammation, allowing for precise treatment and minimal side effects.
- Short treatment time: Laser therapy sessions are typically short and can be completed in just a few minutes, making it a convenient treatment option for busy individuals.

“As a medical professional, I highly recommend Smart Ice high power laser therapy machine as a safe and effective treatment option for reducing inflammation. This non-invasive treatment uses advanced laser technology to stimulate cellular activity, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair. I have seen firsthand how this therapy can benefit patients suffering from a variety of inflammatory conditions, including arthritis, tendinitis, and other musculoskeletal injuries. Patients have reported significant reductions in pain and swelling, as well as improved range of motion and faster healing times.”
—— Dr John Smith
Scientific Support
Abstracts Worth Recommending
[1] Ottaviani, G., Gobbo, M., Sturnega, M., Martinelli, V., Mano, M., Zanconati, F., … & Zacchigna, S. (2013). Effect of class IV laser therapy on chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis: a clinical and experimental study. The American journal of pathology, 183(6), 1747-1757.
[2] Aimbire, F., Albertini, R., Pacheco, M. T. T., Castro-Faria-Neto, H. C., Leonardo, P. S. L. M., Iversen, V. V., … & Bjordal, J. M. (2006). Low-level laser therapy induces dose-dependent reduction of TNFα levels in acute inflammation. Photomedicine and laser surgery, 24(1), 33-37.
[3] Alves, J. C., Jorge, P., & Santos, A. (2023). The Effect of Photobiomodulation Therapy on Inflammation Following Dental Prophylaxis. Journal of Veterinary Dentistry, 08987564221150525.
[4] Cassano, P., Petrie, S. R., Hamblin, M. R., Henderson, T. A., & Iosifescu, D. V. (2016). Review of transcranial photobiomodulation for major depressive disorder: targeting brain metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurogenesis. Neurophotonics, 3(3), 031404-031404.
[5] Clemente, A. M., Rizzetto, L., Castronovo, G., Perissi, E., Tanturli, M., Cozzolino, F., … & Monici, M. (2015). Effects of near-infrared laser radiation on the survival and inflammatory potential of Candida spp. involved in the pathogenesis of chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 34, 1999-2007.
[6] Rodrigues de Morais, N. C., Barbosa, A. M., Vale, M. L., Villaverde, A. B., de Lima, C. J., Cogo, J. C., & Zamuner, S. R. (2010). Anti-inflammatory effect of low-level laser and light-emitting diode in zymosan-induced arthritis. Photomedicine and laser surgery, 28(2), 227-232.
[7] Ludovichetti, F. S., Costa, G., Signoriello, A. G., Stellini, E., Zerman, N., Biffi, A., & Mazzoleni, S. (2023). Evaluating high power laser therapy (HPLT) as treatment for chemotherapy‐induced oral mucositis in paediatric patients with oncohematological diseases. International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry.
THE SCIENCE AND EVIDENCE BACK IT
Laser therapy in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy: a pilot study. Photomedicine and laser surgery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18248158/
Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30572425/
Laser therapy of muscle injuries. Lasers in medical science
Medical lasers
Professional CLASS 4 high-power laser therapy machine
Home use
Portable handheld cold laser therapy device
Veterinary use
Laser therapy machine, shockwave physical therapy, widely used in animals