Page Contents
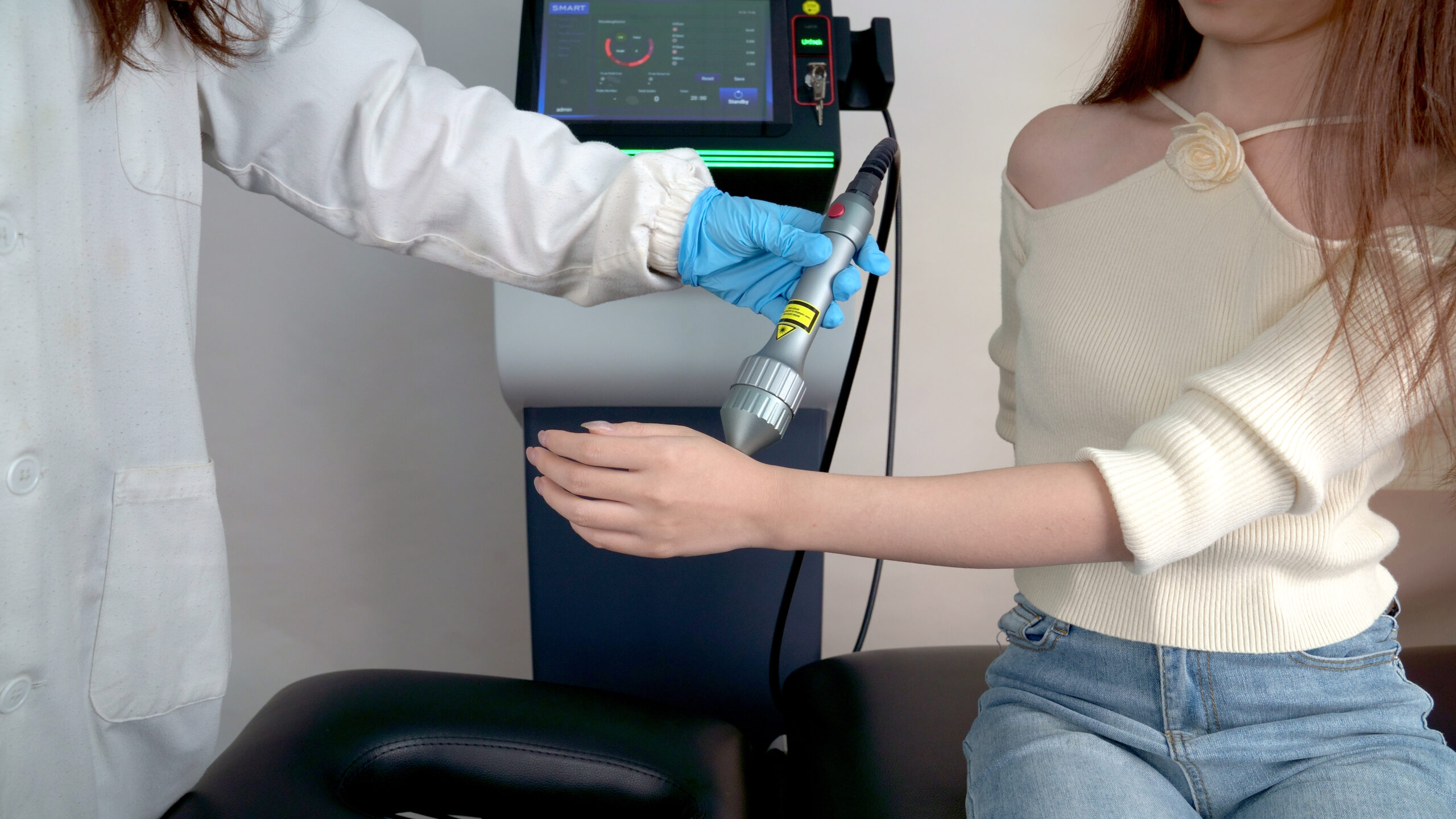
Class 4 lasers are powerful devices used in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and research. They are capable of emitting high-energy beams and are classified based on their potential hazards. When it comes to medical applications, such as surgical procedures or therapeutic treatments, the regulatory oversight by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) becomes crucial in ensuring their safety and effectiveness.
Understanding Class 4 Lasers
Experts categorize Class 4 lasers based on their output power and potential hazards. High-powered lasers like Class 4 lasers are capable of cutting, welding, and performing therapeutic treatments such as laser therapy and surgical procedures. Due to their intensity, Class 4 lasers can pose risks if not used correctly.
FDA Regulation of Class 4 Lasers
The FDA plays a key role in regulating medical devices, including lasers, to safeguard public health. Class 4 lasers used for medical purposes, such as surgical procedures or therapeutic treatments, fall under FDA oversight. It’s important to note that the FDA has not approved or cleared all Class 4 lasers.
FDA Approval Process for Medical Lasers
Manufacturers of medical lasers, including Class 4 lasers used in healthcare settings, are required to obtain FDA clearance or approval before marketing their devices. The FDA evaluates these lasers based on factors such as safety, performance, labeling, and intended use. Clearance or approval indicates that the device has met FDA standards for safety and efficacy.
Differentiating FDA Cleared vs. FDA Approved
It’s crucial to understand the distinction between FDA clearance and FDA approval:
- FDA Cleared: A laser device that is FDA cleared has undergone a review process to demonstrate its safety and effectiveness for specific indications. This typically applies to medical lasers used for therapeutic purposes, such as laser therapy for pain management or dermatological treatments.
- FDA Approved: FDA approval is a more rigorous process reserved for devices that are considered high-risk or have a significant impact on health. Class 4 lasers used for surgical procedures, such as laser eye surgery or laser ablation, may require FDA approval.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Not all Class 4 lasers have FDA approval, but FDA-cleared medical lasers follow strict safety guidelines. Healthcare providers and laser operators should follow established protocols, undergo training, and use appropriate safety measures, including protective eyewear, to minimize risks to patients and operators.
Conclusion: Navigating Class 4 Laser Regulation
In conclusion, Class 4 lasers used for medical purposes are subject to FDA regulation, with devices requiring FDA clearance or approval depending on their intended use and risk level. Healthcare providers should verify the regulatory status of Class 4 lasers and ensure compliance with FDA guidelines to maintain safety and efficacy in laser-based procedures. Understanding the FDA’s role in regulating Class 4 lasers is crucial for informed decision-making and responsible use across various industries.