Page Contents
Photobiomodulation laser therapy (PBMT) is an innovative and non-invasive treatment that uses specific wavelengths of light to interact with tissue, promoting healing, reducing inflammation, and relieving pain. PBMT is based on the principles of photobiomodulation, a process where light energy is absorbed by cells, leading to various therapeutic effects.
Definition and Principles of Photobiomodulation
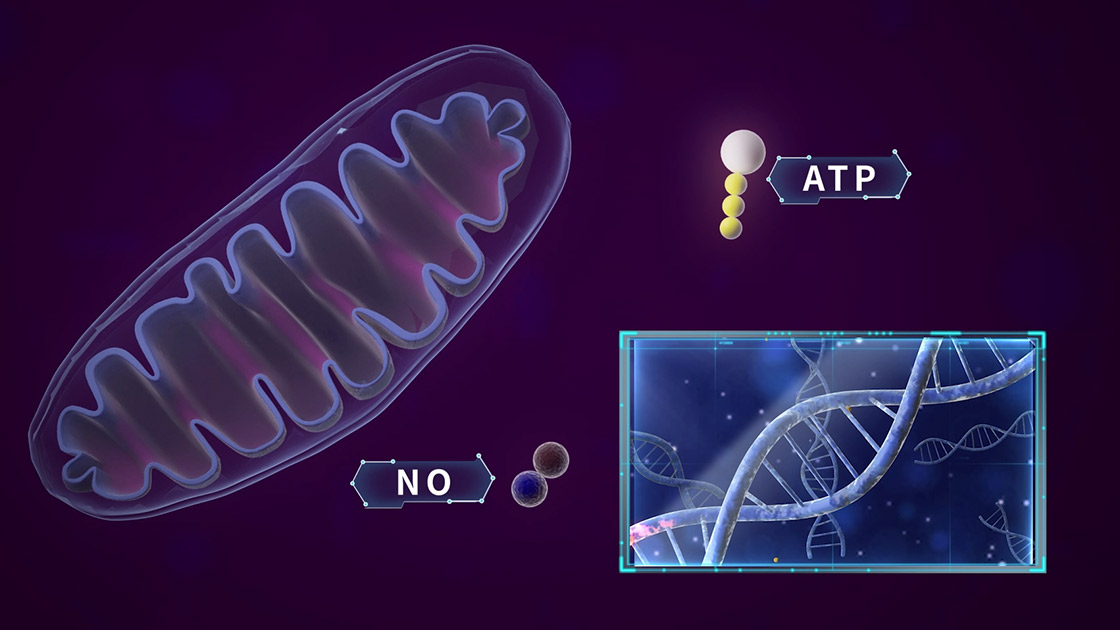
Photobiomodulation refers to the therapeutic use of low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to influence cellular function. This process involves the absorption of light photons by mitochondrial chromophores within cells. These chromophores, particularly cytochrome c oxidase, play a crucial role in cellular respiration and energy production.
When light penetrates the skin and reaches these chromophores, it enhances mitochondrial activity, leading to an increase in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. ATP is the primary energy currency of cells, and its increased production fuels various cellular processes essential for healing and regeneration. Additionally, PBMT can modulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and alter gene expression, contributing to its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects.
Biological Effects of Photobiomodulation Laser Therapy
The biological effects of PBMT are profound and multifaceted. One of the primary effects is the reduction of inflammation. PBMT achieves this by decreasing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines. This modulation helps alleviate chronic inflammation, a common factor in many medical conditions.
PBMT also stimulates collagen production, which is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration. Collagen is a major component of connective tissues, and its enhanced production aids in wound healing and the restoration of damaged tissues. Furthermore, PBMT promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which improves blood flow and oxygen supply to the treated areas, accelerating the healing process.
Pain relief is another significant benefit of PBMT. The therapy modulates pain pathways by reducing the sensitivity of nerves and decreasing the levels of pain mediators like substance P. This results in reduced pain perception and improved patient comfort.
Clinical Applications
PBMT has a wide range of clinical applications, making it a versatile tool in modern medicine. It is particularly effective in treating chronic pain and musculoskeletal conditions, such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and lower back pain. Patients suffering from these conditions often experience significant pain relief and improved mobility following PBMT.
Wound healing is another prominent application of PBMT. The therapy has been shown to accelerate the healing of acute and chronic wounds, including diabetic ulcers and surgical incisions. By enhancing collagen production and angiogenesis, PBMT facilitates faster and more efficient tissue repair.
In dermatology, PBMT is used for treating various skin conditions, including acne, psoriasis, and eczema. It helps reduce inflammation and promotes skin regeneration, leading to clearer and healthier skin. Additionally, PBMT is employed in cosmetic applications to improve skin texture, reduce wrinkles, and promote hair growth.
Benefits and Efficacy of Photobiomodulation Laser Therapy
The benefits of PBMT are numerous and well-documented. One of the most significant advantages is its non-invasive nature. PBMT does not involve any surgical procedures or incisions, making it a safer alternative to more invasive treatments. Patients can undergo PBMT without the risks associated with surgery, such as infections and prolonged recovery times.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of PBMT in various medical conditions. Patients often report noticeable improvements in pain levels, inflammation, and overall quality of life. The therapy’s ability to stimulate cellular processes and promote natural healing makes it a valuable tool in both acute and chronic conditions.
Safety and Best Practices
PBMT is considered a safe treatment option with minimal side effects. Common side effects are usually mild and transient, including redness and slight discomfort at the treatment site. Serious complications are rare, making PBMT suitable for a wide range of patients.
To ensure the safe and effective use of PBMT, it is essential to follow best practices. Practitioners should receive proper training and certification to operate PBMT devices. They should also adhere to established treatment protocols and guidelines, tailoring the therapy to each patient’s specific needs.
Regular maintenance and calibration of PBMT devices are crucial to maintaining their efficacy and safety. Practitioners should stay updated on the latest research and advancements in PBMT to provide the best possible care to their patients.
In conclusion, photobiomodulation laser therapy offers a powerful, non-invasive solution for enhancing healing and reducing pain. Its ability to stimulate cellular processes and promote natural healing makes it a valuable tool in modern medicine. By understanding the principles, biological effects, clinical applications, and best practices associated with PBMT, healthcare professionals can effectively harness its potential to improve patient outcomes.